 |
Plastic Molding in China |
 |
Plastic Injection Molding Design
Basics of Plastic Injection Molding Design
Our basic guidelines for plastic injection molding include important design considerations to help improve part moldability, enhance cosmetic appearance, and reduce overall production time.
Mould Design

The glimpse of designing office

Review before opening mould
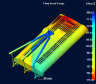
FLOW FRONT
TEMP
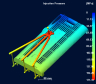
INJECTION
PRESSURE
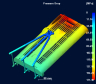
PRESSURE DROP
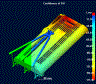
CONFIDENCE
OF FILL

SOLID MODEL
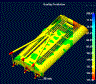
QUALITY
PREDICTION
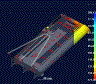
WELD LINES
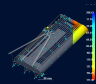
AIR TRAPS
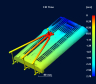
FILL TIME
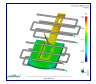
Temperature
Difference Part
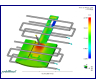
Time to
Freeze Part
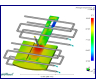
Average
Temperature Part
Quality Control

High precision projector

Surface accuracy

Two-dimensional survey

Three-dimensional survey
Let our custom injection molding engineers help you design the injection molded parts you need. We specialize in tough custom molding jobs where the design, choice of plastic, mold building and flow analysis are critical to production.
What is Plastic Injection Molding?
The plastic injection molding takes place when a thermoplastic or thermoset plastic material is fed into a heated barrel, mixed, and forced into the metal mold cavity where it cools and hardens before being removed.
Mold and die are used interchangeably to describe the tooling applied to produce plastic parts. They are typically constructed from pre-hardened steel, hardened steel, aluminum, and/or beryllium-copper alloy. Of these materials, hardened steel molds are the most expensive to make, but offer the user a long lifespan, which offsets the cost per part by spreading it over a larger quantity.
For low volumes or large components, pre-hardened steel molds provide a less wear-resistant and less expensive option. The most economical molds are produced out of aluminum.
6 Common Thermoplastics Used In Plastic Injection Molding
Thermoplastic injection molding is the most common way to manufacture parts. Below are the most common thermoplastics used in injection molding.
1. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), is an opaque thermoplastic and amorphous polymer. In addition to molded plastics, ABS is used in drain pipe systems, plastic clarinets, golf club heads, automotive parts, common appliances in a kitchen, LEGO bricks, and many other products.
2. Polyethylene is a thermoplastic polymer with variable crystalline structure and an extremely large range of applications depending on the specific type.The advantages of polyethylene are high levels of ductility, tensile strength, impact resistance, resistance to moisture absorption, and recyclability.The primary uses of polyethylene are plastic bags, plastic films, containers including bottles, and geomembranes.
3. Polycarbonate (PC) plastics are a naturally transparent amorphous thermoplastic. PC is commonly used for greenhouses, digital disks like DVDs, eyewear lenses, medical devices, automotive components, and cellular phones.
4. Nylon material is used in a large range of different applications. This material produces plastic parts used in many industries such as:Medical products,Automotive products,Sports equipment,Apparel and footwear,Industrial components.
5. High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) is a popular and tough plastic that is in the Polystyrene family. It is highly flammable, but there are flame retardant and high gloss grades that are commonly used for injection molding.
6. PP (polypropylene) is a very dynamic plastic and has been compounded for a wide range of properties. It can be commonly found in household goods such as utensils, athletic apparel, area rugs, and automotive parts such as car batteries.
Plastic Injection Molding Process
The plastic injection moulding process produces large numbers of parts of high quality with great accuracy, very quickly. The plastic injection molding process uses a granular plastic that is gravity fed from a hopper. A screw-type plunger forces the material into a heated chamber, called a barrel, where it is melted. The plunger continues to advance, pushing the polymer through a nozzle at the end of the barrel that is pressed against the mold. The plastic enters the mold cavity through a gate and runner system. After the cavity is filled, a holding pressure is maintained to compensate for material shrinkage as it cools.
At this same time, the screw turns so that the next shot is moved into a ready position, and the barrel retracts as the next shot is heated. Because the mold is kept cold, the plastic solidifies soon after the mold is filled. Once the part inside the mold cools completely, the mold opens, and the part is ejected. The next injection molding cycle starts the moment the mold closes and the polymer is injected into the mold cavity.
5 Major Advantages of Plastic Injection Molding
1. High Efficiency- Fast Production
Once the injection molds have been designed to the customer’s specifications and the presses pre-programmed, the actual molding process is very quick compared to other methods of molding, and the high production output rate makes it even more efficient and cost-effective. Speed depends on the complexity and size of the mold but only about 15-120 seconds pass between each cycle time.
2. Detailed Features and Complex Geometry
The injection molds are subjected to extremely high pressure. As a result the plastic within the molds is pressed harder against the mold compared to any other molding process. Due to this excessively high pressure, it is possible to add a large amount of details into the design of the part.
With the right design, parts can be made consistently and with quality. Without a good design, costly processing mistakes can be made
3. Enhanced Strength
Strength is one of the key factors that need to be determined when designing a plastic injection molded part.
In plastic injection molding, it is possible to use fillers in the injection molds. These filler reduce the density of the plastic while it being molded and also help in adding greater strength to the part after it has been molded.
4. Flexibility- Material and Color
One of the major advantages of using plastic injection molding for manufacturing parts is the ability to use different types and colors of plastic simultaneously. This can be done with the help of co-injection molding. Due to the wide variety of both, the possibilities are almost endless.
5. Save Manufacturing Costs
Labor costs are typically relatively low in plastic injection molding, in comparison with other types of molding. The ability to produce the parts at a very high level with a high output rate helps with its cost efficiency and effectiveness.
Plastic injection molding is an automated process. Automation helps to reduce manufacturing costs, as the overheads are significantly reduced.